Dashboard UI Guide
The EverTask dashboard is a modern React interface that gives you complete visibility into your background tasks. Think of it as your mission control for monitoring task execution, debugging failures, and understanding performance patterns.
Note: The dashboard is currently read-only (v3.3). You can view, analyze, filter, and export all task data, but task management operations (stop, restart, cancel) will be added in future releases.
Quick Access:
URL: http://localhost:5000/evertask-monitoring
Default Credentials: admin / admin
What You Can Do
The dashboard helps you answer critical questions about your background tasks:
- “What’s happening right now?” - See tasks in progress, recent completions, and failures in real-time
- “Why did this task fail?” - Drill into execution logs with full stack traces and structured logging
- “Is my system healthy?” - Monitor success rates, execution times, and queue metrics at a glance
- “Which tasks are slow?” - Analyze performance trends and identify bottlenecks
- “How reliable are my recurring tasks?” - Track execution history across all attempts
Main Views
Overview Dashboard
Your starting point shows the big picture: total tasks, success rates, active queues, and average execution times. Time-based charts help you spot trends (hourly spikes, daily patterns, weekly anomalies). Queue cards give you instant health checks with color-coded success rates (green = healthy, yellow = watch, red = investigate).
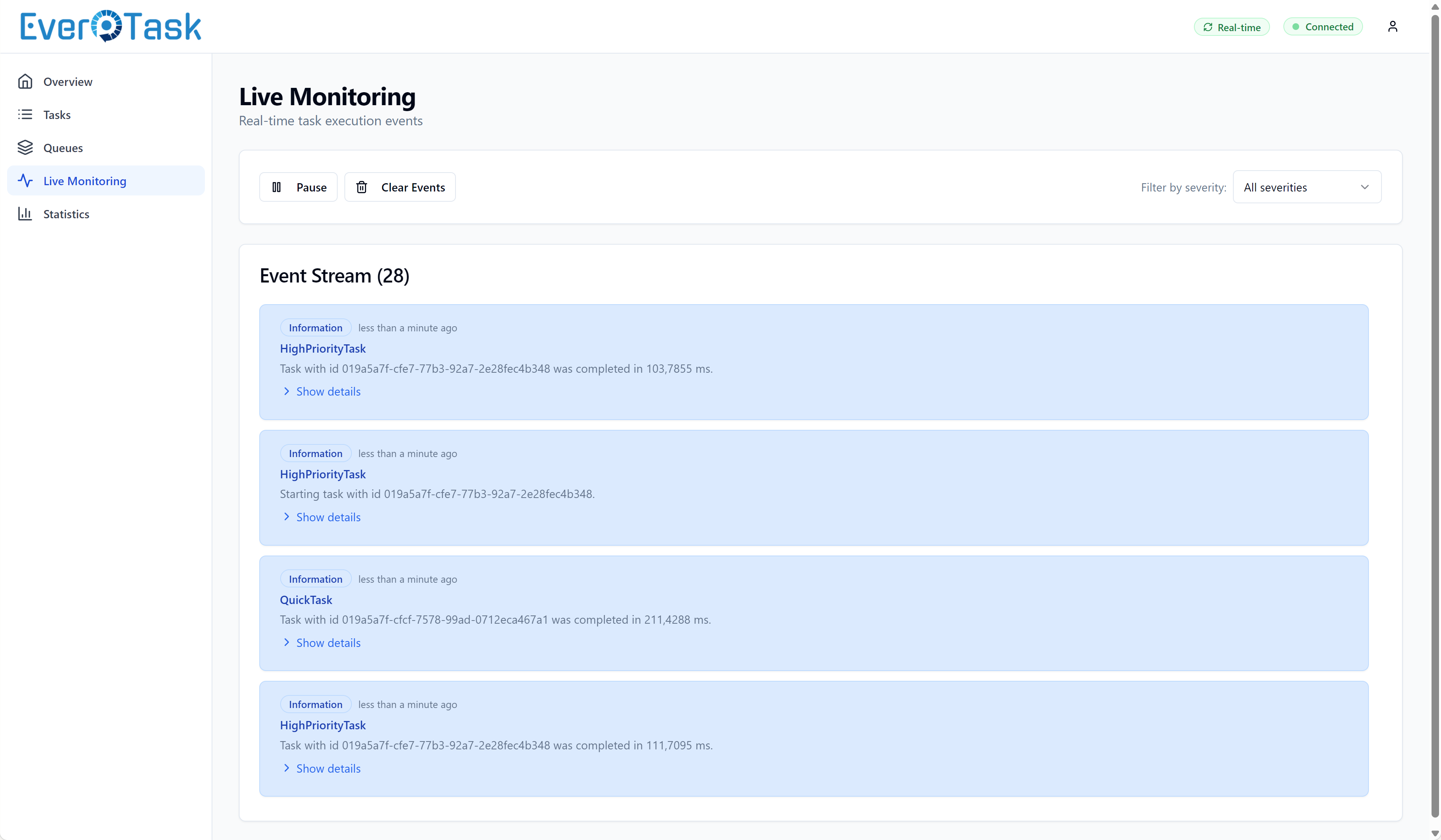
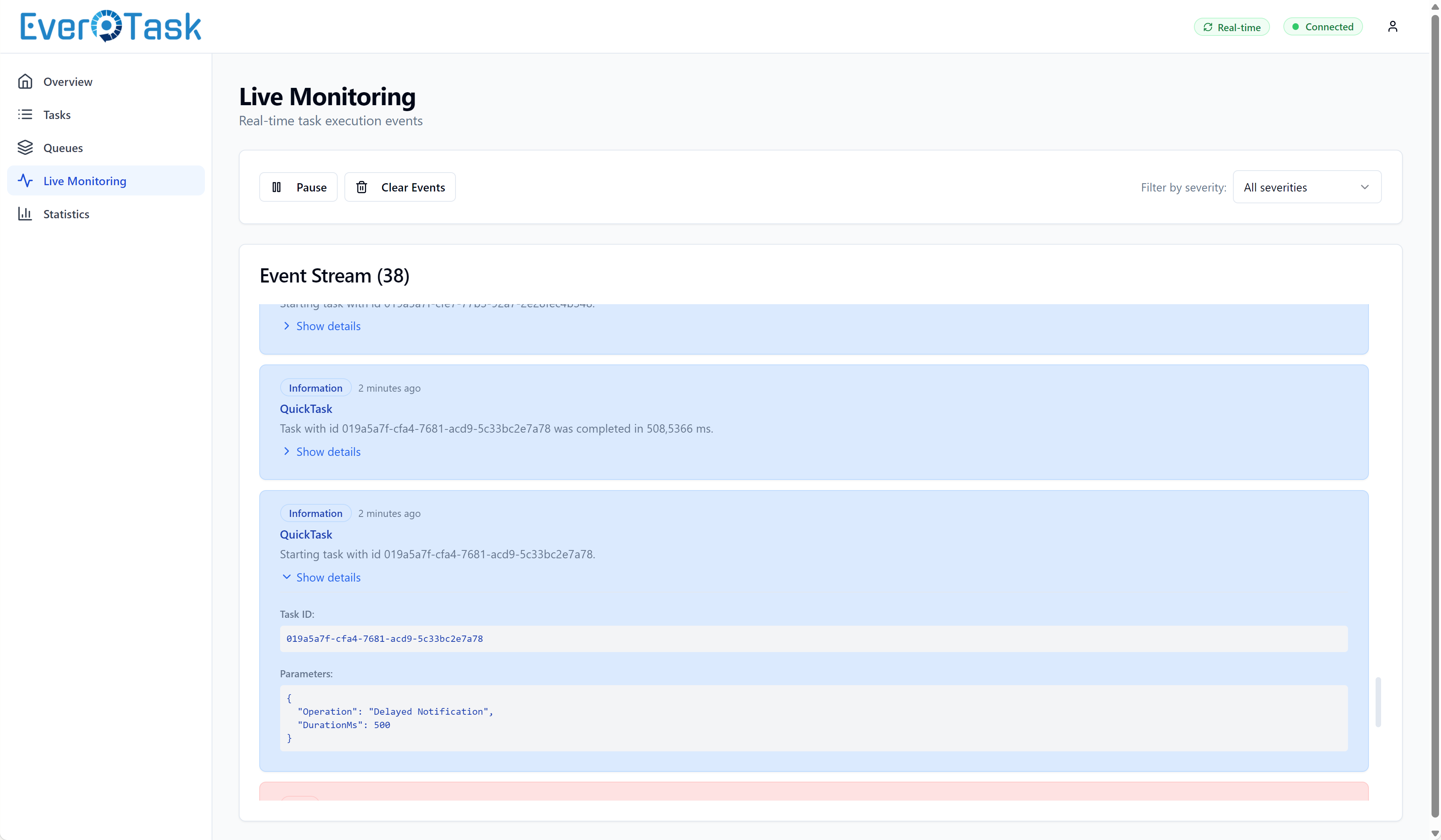
The Recent Activity feed shows the last 50 events as they happen, so you can watch tasks flow through the system in real-time.
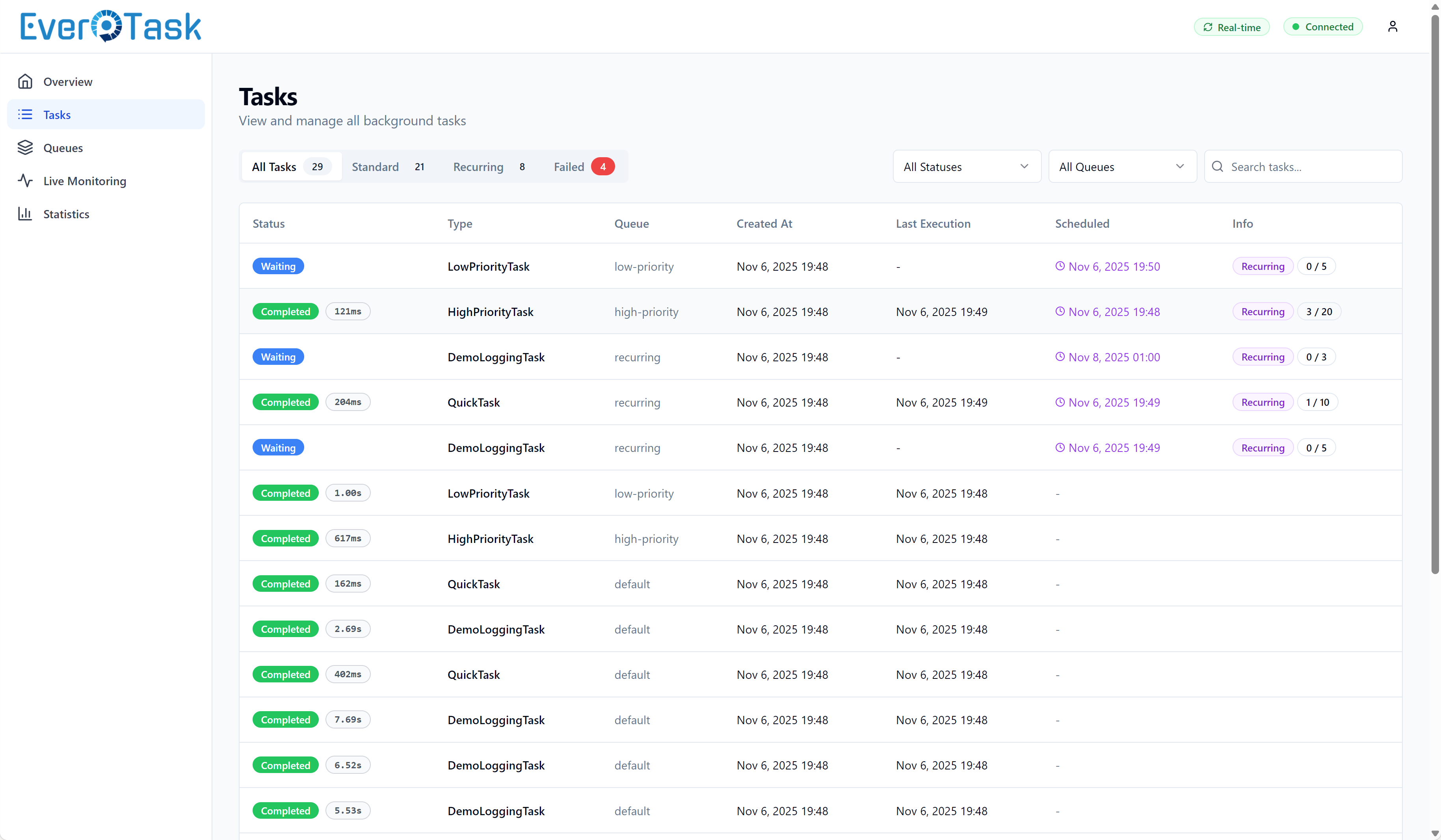
Task List & Filtering
Find any task quickly with powerful filtering: status (Queued, In Progress, Completed, Failed, Cancelled), queue name, task type, or date range. Combine filters to narrow down exactly what you need: “Show me all failed payment tasks from yesterday in the critical queue.”
Search is instant and works across task IDs, types, and parameters. Pagination keeps things fast even with millions of tasks in storage.
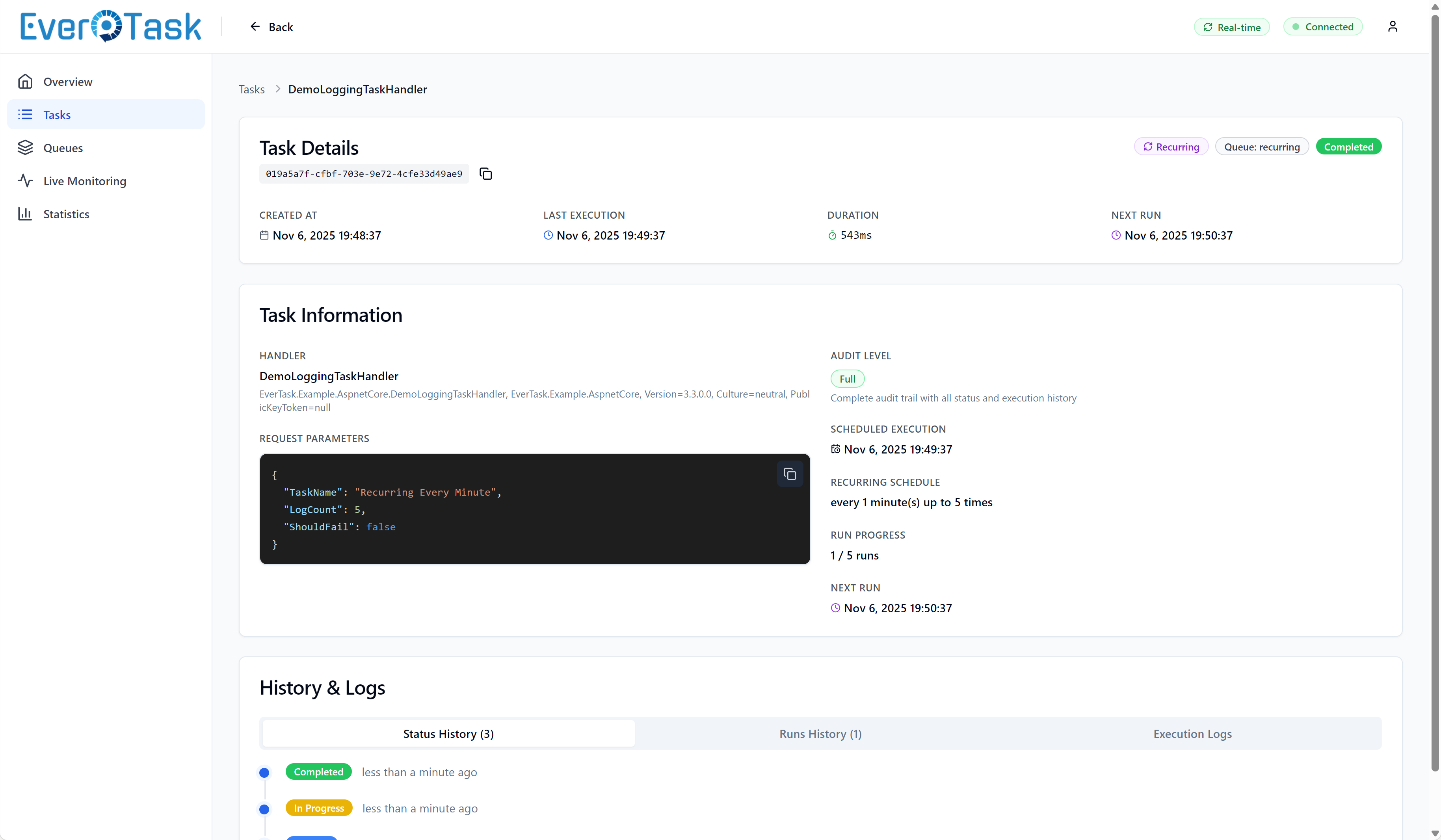
Task Details
Click any task to see everything about its lifecycle. The modal view has three tabs:
Status History shows every state transition (Queued → InProgress → Completed/Failed) with timestamps. Perfect for understanding “when did this task actually start?” or “how long was it queued?”
Execution History is especially valuable for recurring tasks. See all execution attempts, their durations, and outcomes. Quickly spot if a recurring task that usually takes 2 seconds suddenly took 30 seconds on the last run.
Execution Logs is your debugging powerhouse. If you enabled persistent logging, you’ll see a terminal-style viewer with color-coded log levels (Info in blue, Warnings in yellow, Errors in red). Stack traces get syntax highlighting, and you can export logs to JSON/CSV for deeper analysis.
Queue Metrics
Each queue gets its own card showing task distribution (how many queued, running, completed, failed). Success rate percentages with color indicators help you spot troubled queues instantly. Click a queue card to filter the task list to that queue’s tasks.
Multi-queue systems shine here: you can see at a glance if your “critical” queue is healthy while your “background” queue has some failures that need investigation.
Analytics & Trends
The Statistics page helps you understand patterns over time. Success rate trends show if your system is getting more stable or degrading. Task type distribution reveals which handlers run most frequently (maybe you didn’t realize your health check runs 10,000 times a day).
Execution time analysis is where you find performance bottlenecks. A sortable table shows average, min, and max execution times per task type. Color-coded indicators highlight slow tasks (>5s average = red flag). This helps you prioritize optimization efforts: “Our email task averages 8 seconds, but our payment task averages 50ms – let’s optimize emails.”
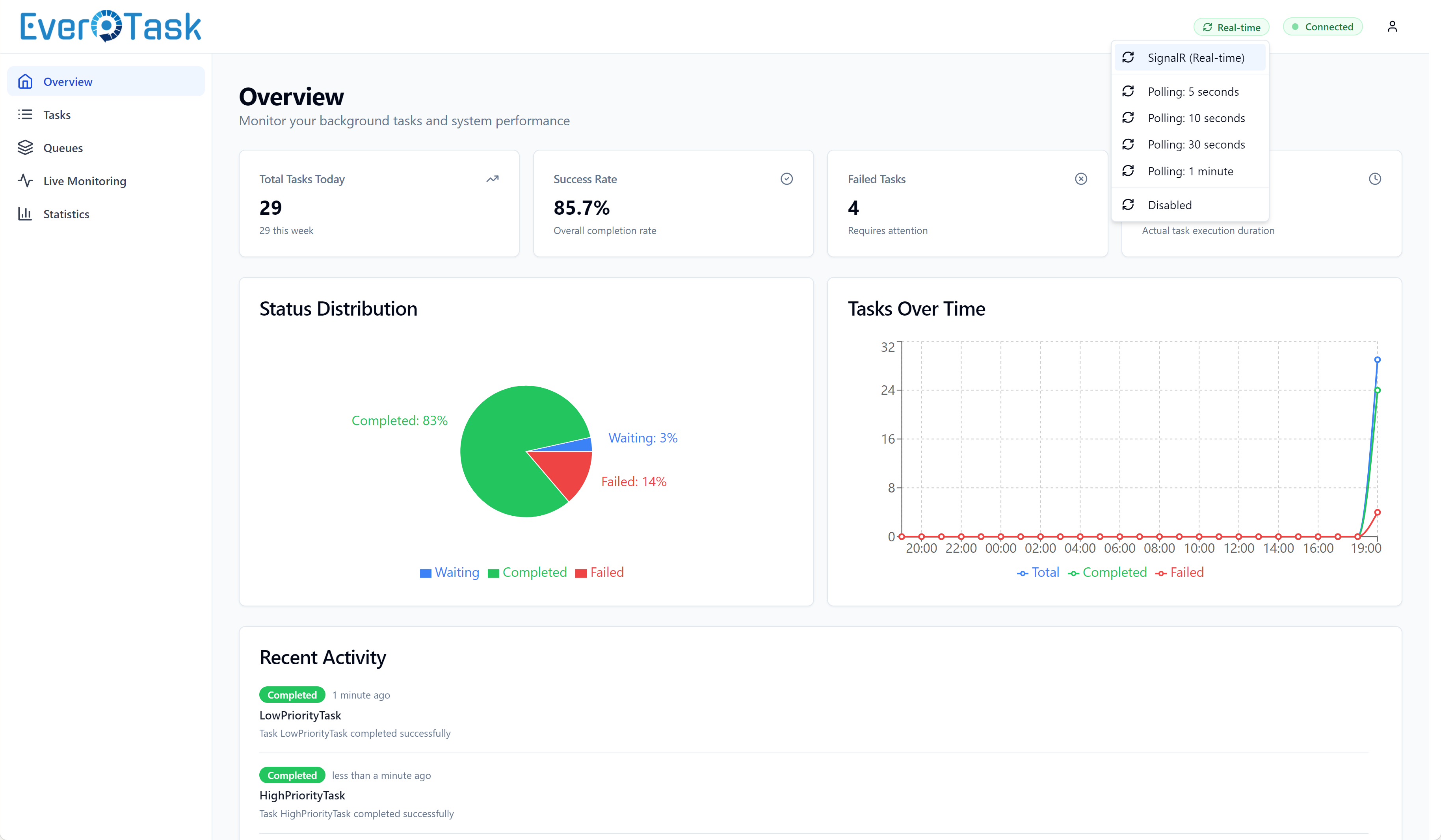
Real-Time Updates
The dashboard uses SignalR for intelligent real-time updates. Instead of polling every few seconds (which wastes bandwidth and hammers your API), the dashboard only refreshes when something actually changes.
How It Works:
When a task completes, fails, or changes status, EverTask broadcasts a SignalR event. The dashboard receives the event and invalidates its cache, triggering a fresh data fetch. Multiple rapid events (like during a task burst) are debounced to prevent API spam – if 100 tasks complete in 2 seconds, you get one refresh, not 100.
Configure Responsiveness:
.AddMonitoringApi(options =>
{
options.EventDebounceMs = 1000; // Wait 1 second before refreshing (default)
// 300ms: Very responsive (low-volume)
// 500ms: Balanced (moderate responsiveness)
// 1000ms: Conservative (high-volume, best performance)
});
Connection Status:
The header shows your SignalR connection status with color-coded indicators (green = connected, yellow = connecting, red = disconnected). If SignalR drops, the dashboard automatically falls back to polling every 30 seconds. You can force a refresh anytime with the refresh button.
This architecture reduces network traffic dramatically while keeping the UI feeling instant. No more stale data, no more excessive polling.
Screenshots
See the dashboard in action with these 10 screenshots showing all major features:
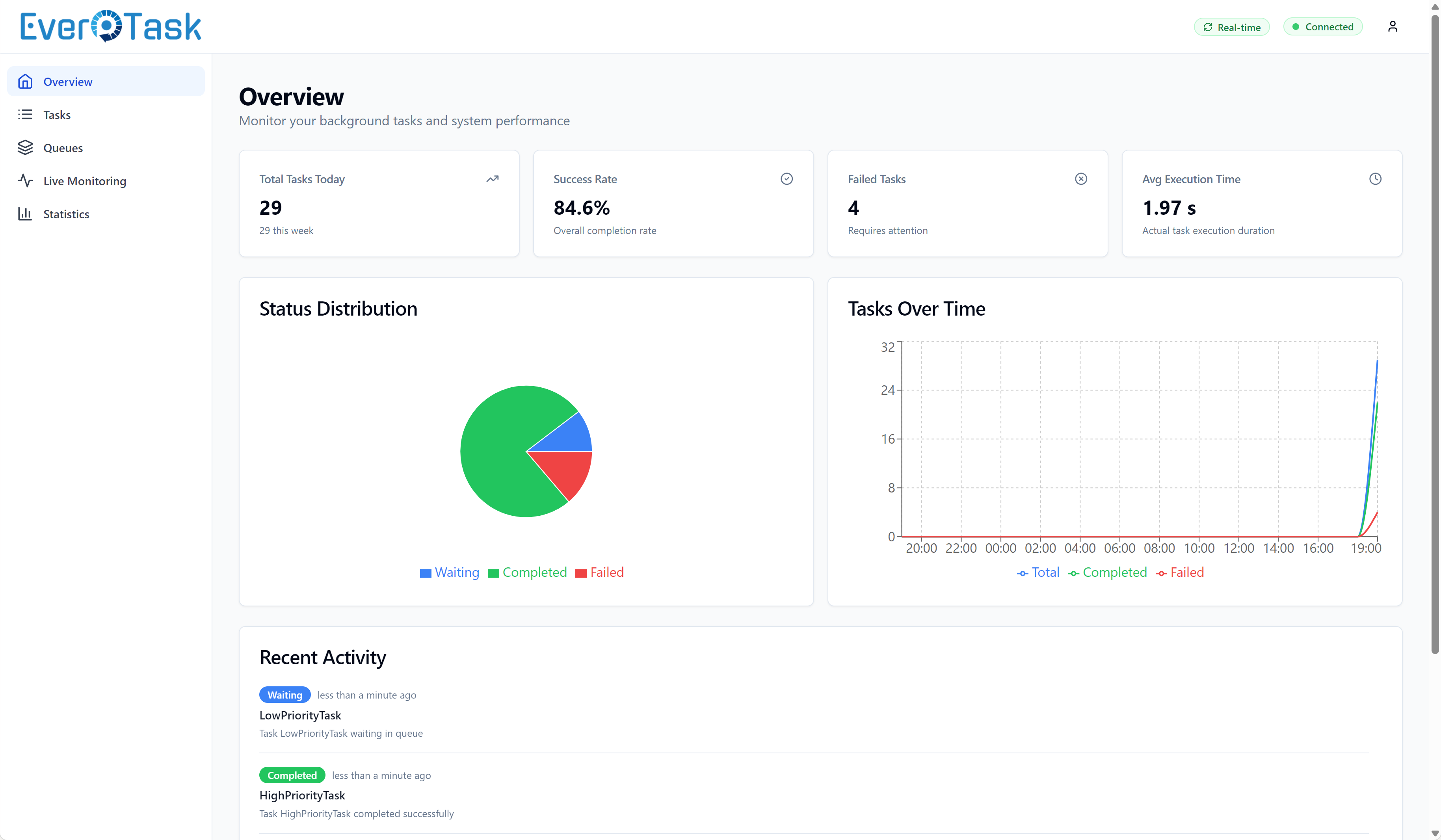
Overview dashboard with real-time metrics and activity charts
Task list with advanced filtering and search
Task detail modal with parameters and execution info
Terminal-style execution logs with color-coded severity
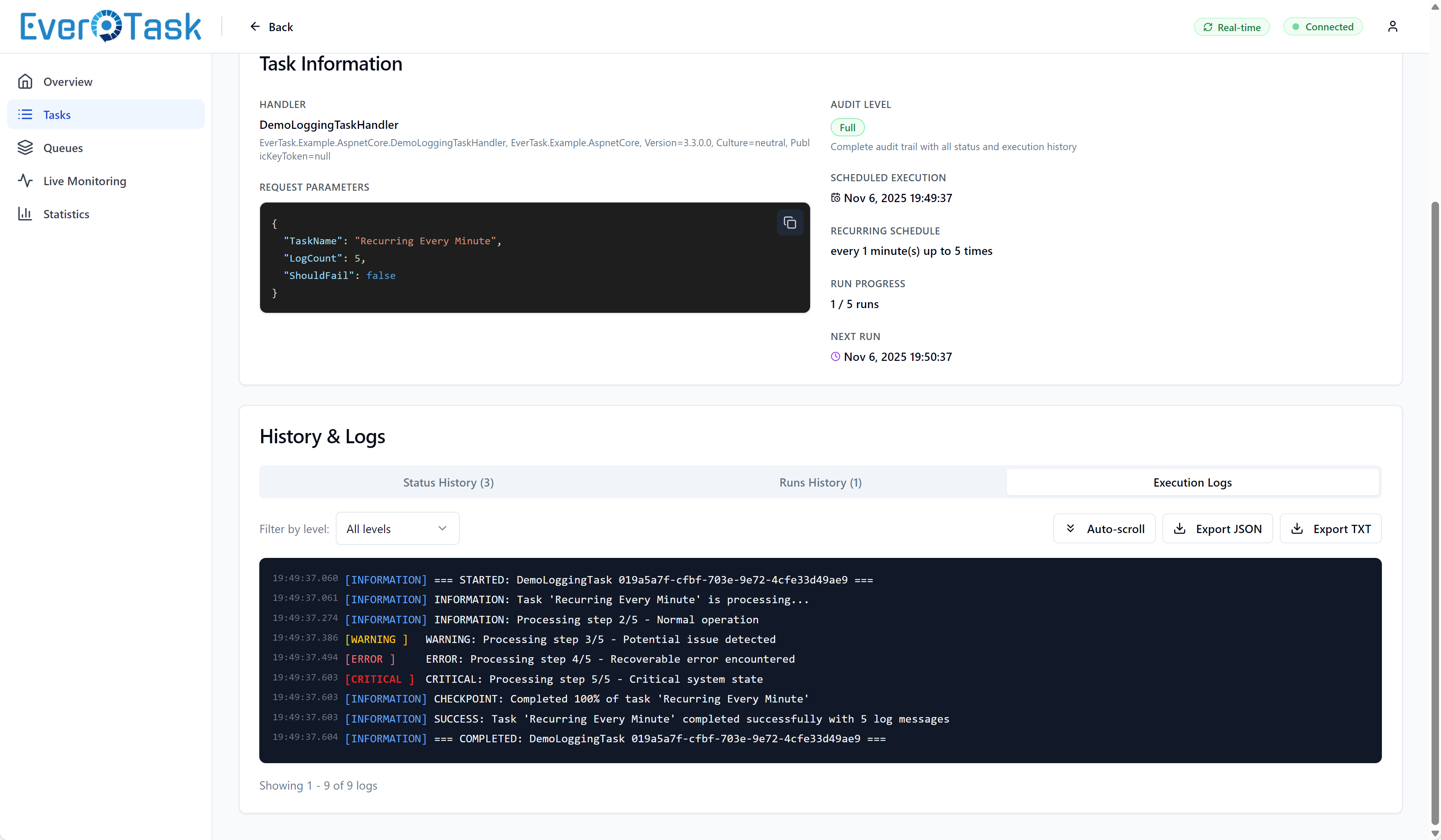
Complete audit trail of status transitions
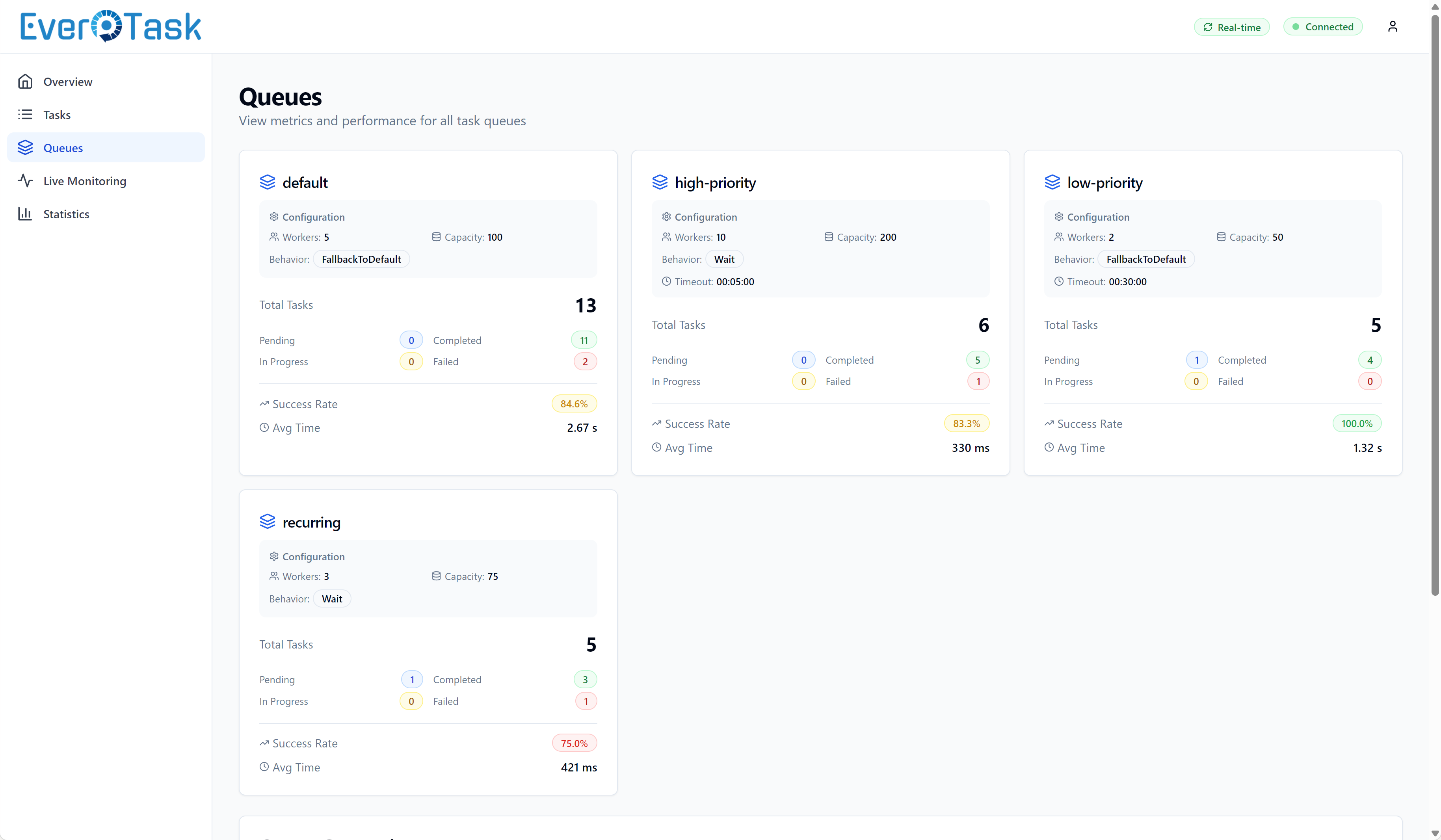
Multi-queue monitoring with success rates
Performance analytics and trends over time
Advanced filtering by status, queue, type, and date
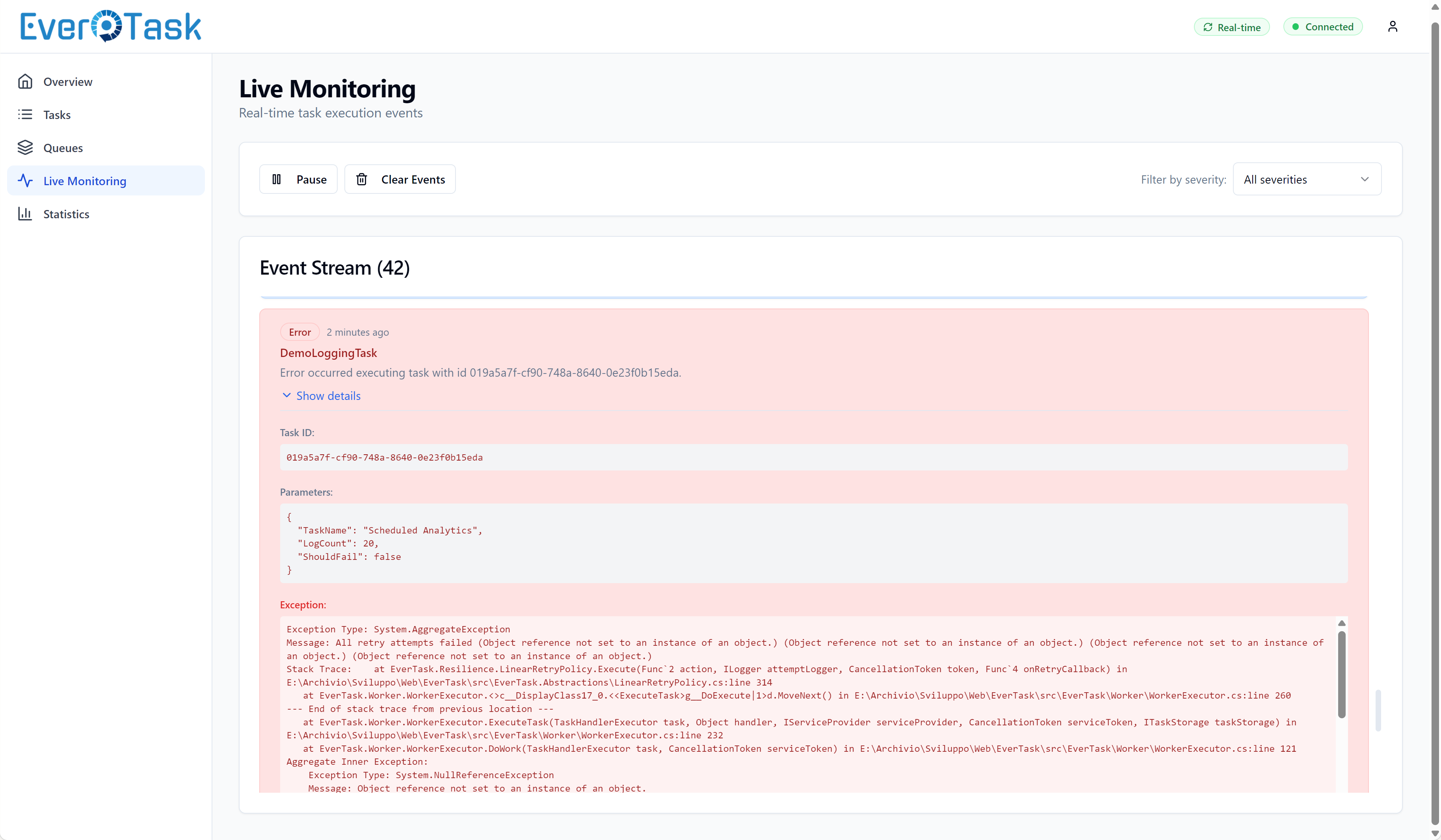
Live updates with SignalR integration
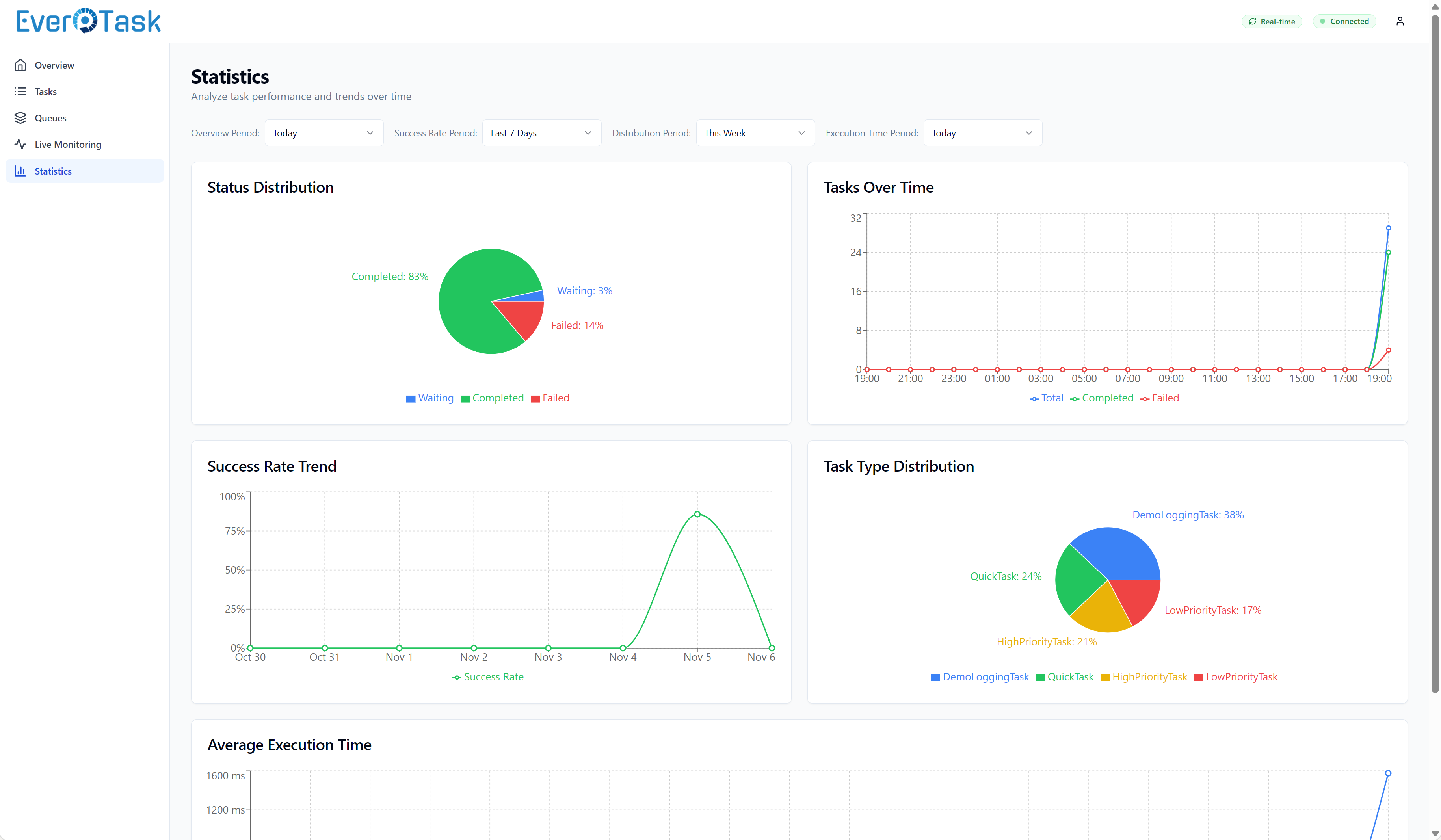
Execution history for recurring tasks
Coming in Future Releases
Task management operations (stop, restart, cancel tasks), runtime parameter editing, and queue management (pause/resume) are planned for future versions.
Next Steps
- Monitoring Dashboard - Setup and configuration
- API Reference - REST API documentation
- Custom Event Monitoring - Event-based integrations
- Task Execution Logs - Log capture configuration